JOEL ÇELA
The COVID-19 pandemic is being associated with what the WHO is calling an “infodemic”, an avalanche of untrue and misleading information. For more than one year during the pandemic, the infodemic has scored a milestone in the massive vaccination process. Fake news have made such an impact that people are refusing vaccination. From a global scale inspection the countries with the highest circulation of misinformation sites are also the ones where individuals refuse to be vaccinated against COVID-19, making the ‘infodemic” one of the most dangerous enemies of public health.
Do the vaccines contain magnets or metals as rumored?
One of the most widespread news about vaccines since the global vaccination process against COVID-19 has started is the questionable content of the injected substance. Online sites that have shared this information (confirmed by international health authorities as fake) include some pictures or even videos that show how coins stick to the injection site. The civic concern that this news has produced has also reached the editorial office of Faktoje. Our followers have sent photos of coins or other metal objects that stick to the arm area where they had their vaccine.
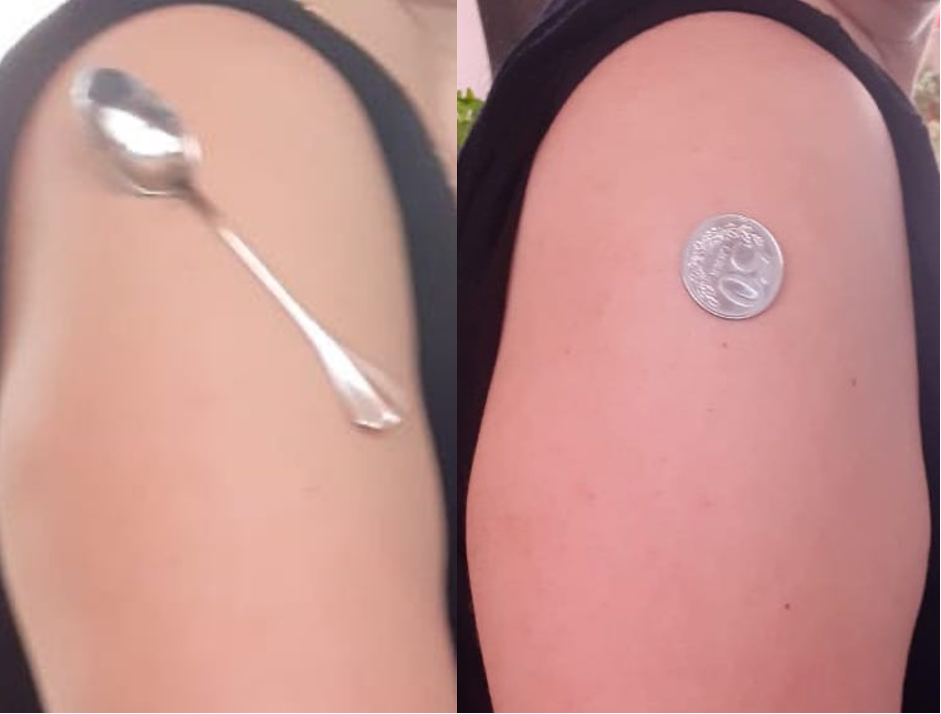
Pictures sent to the editorial office of Faktoje
Newsguard Technologies, the American company (that monitors and identifies online sites for the credibility and transparency of the news they publish) has classified this news to be a fake myth, after several experts of the medical field have dismissed it.
Dr. Stephen Schrantz, an infectious disease specialist at the University of Chicago, has refuted the allegations by calling the videos of people with coins on their shoulders a scam. Speaking for AFP (Agence France-Presse) in May 2021, he stated that there is no way that these videos are true.
“Vaccination against COVID-19 cannot cause arm magnetization. This is a plain and clear scam. There is no way the vaccine can cause this reaction.” – he stated.
Dr. Edward Hutchinson, a lecturer at the Center for Virus Research at the University of Glasgow, stated for Newsweek in May 2021 that the amount of magnetic material had to be large to cause effect.
“That would require placing a large piece of magnetic material under the skin to cause action beyond the skin, in the way it is claimed.”If you want to try it, get a fridge magnet and try to pull some metal, especially very small pieces through the skin between your thumb and forefinger,” he said.
Faktoje contacted a local expert, Dr. Sc. Ilir Alimehmeti, clinical epidemiologist at the Faculty of Medicine in Tirana, who confirmed that magnetization could not be present in COVID-19 vaccines.
“In terms of magnetization, to attract a coin you need a magnet weighing about 1 gr. A magnet weighing 1 gr cannot be found in a transparent solution as in the case of the vaccine, and if I remember correctly the amount of vaccine we get is about 0.3 to 0.5ml. So, if it all were metal, we would see it very clearly. It is clearly an aqueous solution, according to the descriptions with the ingredients that have been stated. “– he stated for Faktoje.
We also asked him if the FDA and EMA certified vaccines contained any metals.
“Neither Pfizer nor AstraZeneca contain metals, according to the statements of the manufacturers and the authorizing authorities.
Meanwhile Sinovac has a very low content of aluminum hydroxide, which increases the effectiveness of the vaccine that is about 1/1000 of the total recommended annual dose, which causes no issues. Thus, is a very low level.” – he concluded.
A lot of fake news = many citizens that refuse the vaccine against COVID-19
One of the most problematic phenomena that has accompanied the almost 2-year period of the COVID-19 pandemic is the flow of false information. The World Health Organization warned us since the very first moments the world came to face this issue by calling it an infodemic and making clear the scale of the risk of this phenomenon.
Newsguard Technologies, an American company that checks news sites and their authenticity, has focused particularly on information about COVID-19 and the vaccination process during the pandemic period. Partnering with WHO it has identified 447 websites around the world that share fake news on COVID-19 and the vaccines. The highest number of these sites is located in the United States, where 274 sites ‘operate’, thus almost half of the ones that operate worldwide.
In Europe, France leads with 57 websites, followed by Germany with 44, Italy with 41 and Great Britain with 20 websites, identified as misleading.
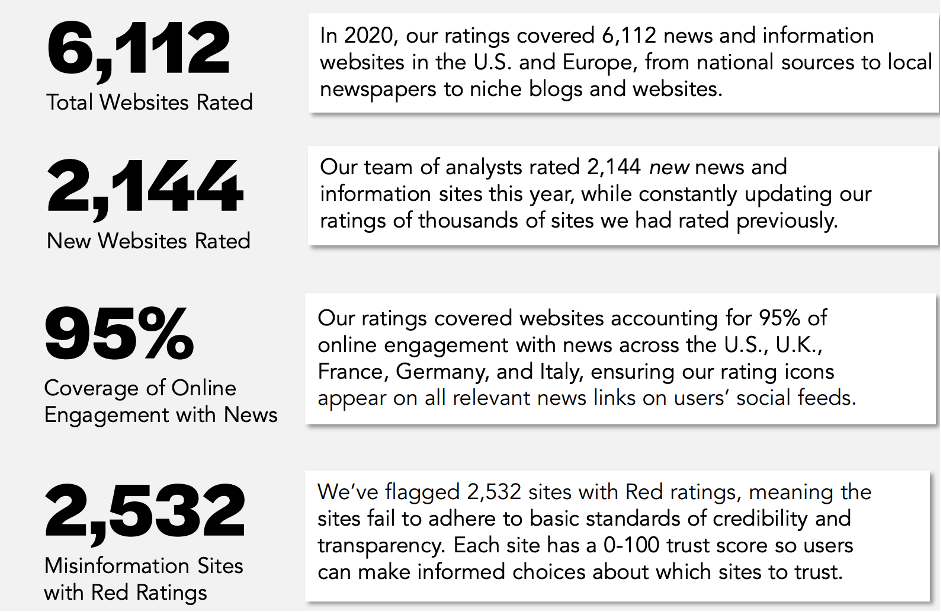
Newsguard’s report for 2020
During 2020, Newsguard has inspected a total of 6,112 websites from the USA and Europe, starting from national media to local newspapers, blogs and other websites. Of this number of sites, 2,144 were new sites compared to the sites considered for inspection in previous years, an interesting indicator for the first year of the COVID-19 pandemic. Newsguard has flagged 2,532 websites, which demonstrates that these sites don’t fulfill even the basic standards of credibility and transparency.

Newsguard’s report for 2020
371 websites were signaled to have been sharing false and dangerous information during the COVID-19 pandemic. Newsguard identified 111 websites that over-shared false information on COVID-19, with an audience of over 51 million followers or likes.
IPSOS has carried out a survey on behalf of the World Economic Forum, published in the end of April 2021, on the percentage of people that were reluctant of taking the vaccine against COVID-19 in different states.
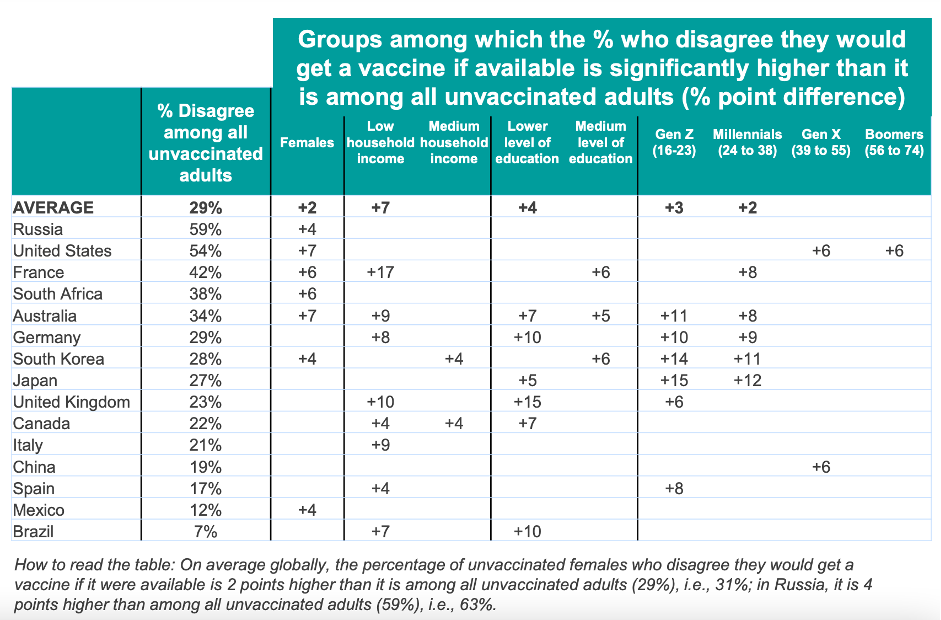
IPSOS survey, published in April 2021
Russia tops the list, with 59% of unvaccinated adults saying they would refuse to receive the vaccine if offered. If we refer to other countries identified by Newsguard with the highest number of online sites that disseminate false information about COVID-19 (USA, France, Germany, Britain, Italy), we will see that the same ranking among them coincides with the percentage of the adult population that refuses to be vaccinated.
The USA, having the highest number of such sites (274) also has the highest vaccine rejection rate among unvaccinated adults (54%).
France, ranked second by Newsguard with 57 sites, also ranks second among these countries for vaccine rejection, with 42%.
Germany, ranked third by number of websites (44) also ranks third for vaccine rejection by country (29%)
The only difference in the ranking is between Italy and the UK, Even though at 41 misinforming websites, Italy has more misinforming websites than the UK (20), it’s vaccine rejection rate is lower (21%) than in the UK (23%).





